As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly integrated into business operations, ensuring their security has become a top priority. To mitigate the unique risks associated with LLMs, solutions like LLM firewalls and prompt shields have emerged. While both aim to enhance the safety of LLMs, their approaches and functionalities differ. This article explores the distinctions and advantages of LLM firewalls, such as Arthur Shield, and prompt shields, exemplified by Llama Guard.
What Are LLM Firewalls?
LLM Firewalls are security tools designed to protect LLM-based applications from malicious inputs and outputs. These firewalls act as a barrier between the user and the LLM, inspecting and filtering prompts and responses to prevent security breaches. LLM Firewalls focus on identifying and blocking attacks such as:
Prompt Injection Attacks: Manipulating the model’s input to extract sensitive data or generate harmful content.
Jailbreak Attacks: Bypassing safety measures to make the model reveal sensitive information or perform unauthorised actions.
Data Leakage: Preventing the model from inadvertently exposing sensitive data in its outputs.
How LLM Firewalls Work
LLM Firewalls analyse both the input and output of the model. They use advanced algorithms, including machine learning models, to detect malicious patterns or content. For instance, Arthur Shield is an AI firewall that uses a scoring engine to classify prompts as benign or malicious. If a prompt is flagged as harmful, the firewall blocks it or modifies it to ensure safety.
Key Features of LLM Firewalls
Real-Time Protection: Filters inputs in real-time to prevent malicious prompts from reaching the LLM.
Output Validation: Sanitises the model’s responses to remove harmful or sensitive content.
Adversarial Robustness: Designed to withstand sophisticated attack techniques like prompt injection.
What Are Prompt Shields?
Prompt Shields, such as Llama Guard, are tools designed to guide the behaviour of LLMs by modifying or restricting the prompts they receive. Unlike firewalls, which focus on blocking malicious inputs, Prompt Shields aim to ensure that the model’s outputs align with ethical guidelines and corporate policies. They operate by:
Defining guardrails for acceptable content.
Restricting the model’s responses to specific topics or tones.
Detecting and blocking harmful prompts before they are processed by the LLM.
How Prompt Shields Work
Prompt Shields evaluate the input prompt and modify it to ensure it adheres to predefined rules. For example, Llama Guard is a language model trained to identify and block prompts that could lead to harmful outputs. It evaluates inputs based on categories like violence, hate speech, or illegal activities, and either allows or blocks the prompt accordingly.
Key Features of Prompt Shields
Guardrails: Define acceptable and unacceptable content based on ethical guidelines or organisational policies.
Few-Shot Learning: Can adapt to new policies with minimal fine-tuning.
Customisation: Allow users to tweak or create new categories for content moderation.
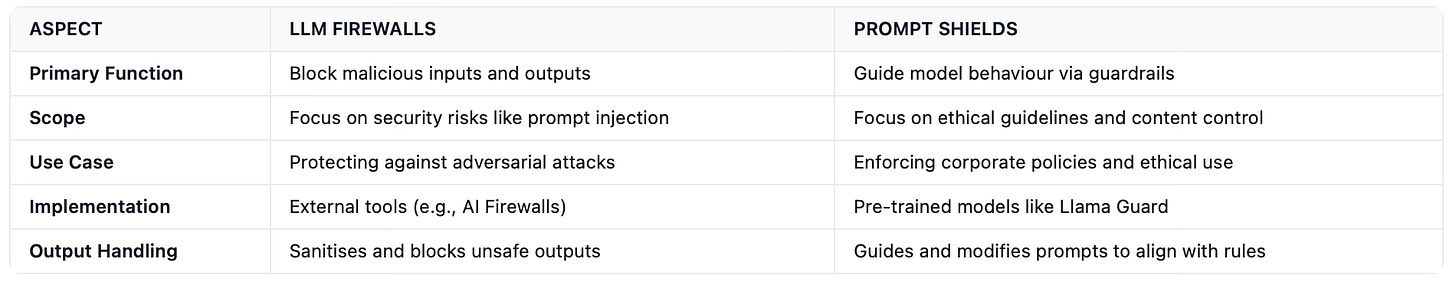
Comparing LLM Firewalls and Prompt Shields
When to Use Each Approach
LLM Firewalls are ideal for organisations prioritising security and data protection. They are particularly useful for enterprise applications where the risk of data breaches or adversarial attacks is high.
Prompt Shields are better suited for scenarios where ethical compliance and content moderation are critical. They are commonly used in customer-facing applications to ensure responses align with brand guidelines and legal requirements.
Both LLM Firewalls and Prompt Shields are critical components of a secure and ethical AI ecosystem. While LLM Firewalls focus on blocking malicious inputs and outputs, Prompt Shields guide the model’s behaviour to align with predefined guidelines. Depending on the use case, organisations may choose one approach or combine both to create a robust security framework.
By understanding the differences and use cases of these tools, developers can protect their LLM applications from security risks while ensuring ethical and responsible AI use.